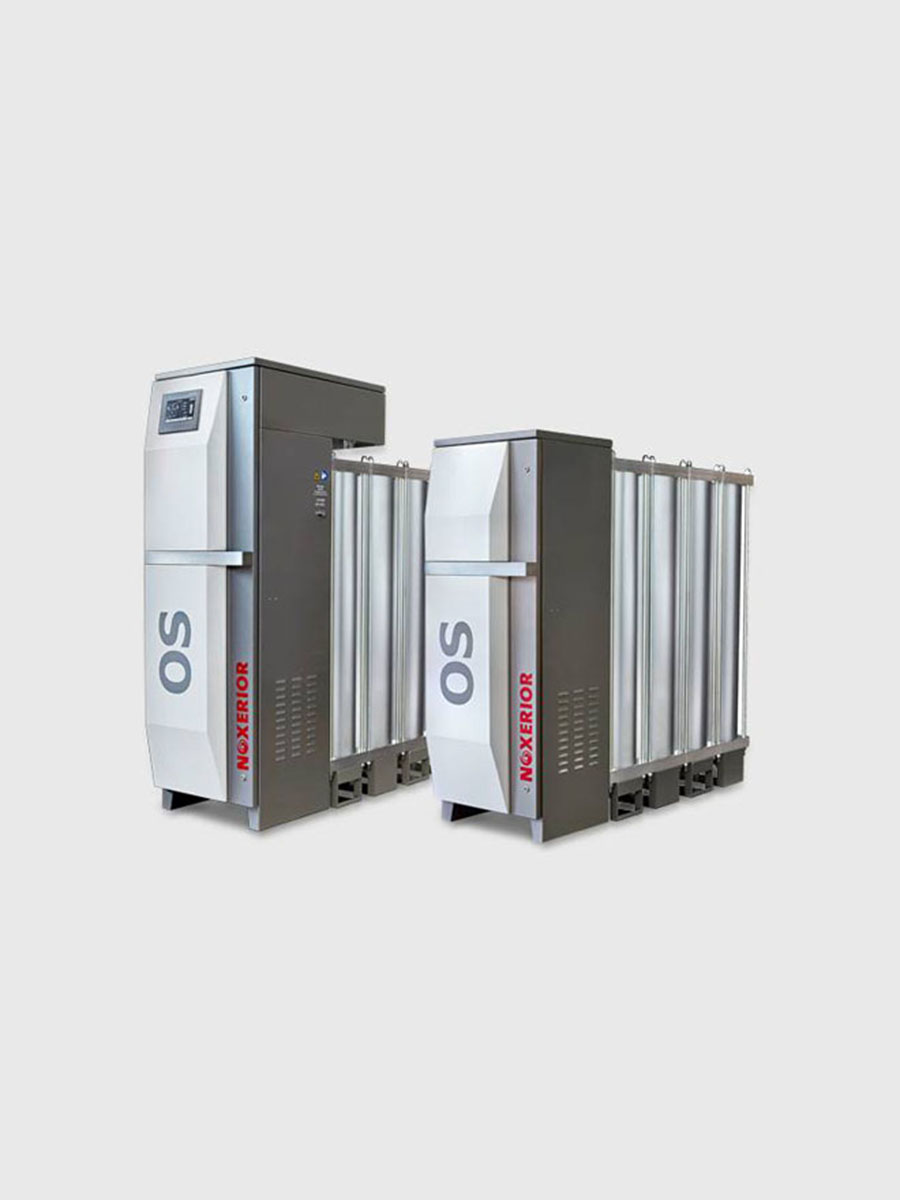
What are oxygen generators?
Devices that produce oxygen, usually for industrial, medical, or environmental uses, are known as oxygen generators. They play vital roles in a variety of contexts, from hospitals that offer respiratory support to isolated areas that need breathable air. These devices use a variety of technologies, but they mostly function on two fundamental ideas: membrane separation and pressure swing adsorption (PSA). Each method has its own advantages and limitations, catering to different user needs.
How do they work?
The most common type of oxygen generator uses pressure swing adsorption (PSA) technology. Zeolite or other adsorbent materials are used in this process to selectively capture nitrogen from the air while permitting oxygen to flow through. As ambient air enters the generator, the adsorbent material effectively concentrates the oxygen content by capturing nitrogen molecules while allowing oxygen molecules to pass through. The adsorbent is then ready for a new cycle when the pressure is finally released, allowing the nitrogen to return to the atmosphere. This method is highly efficient and can produce oxygen concentrations of 90% or more, making it suitable for various medical and industrial applications.
Oxygen Generators use in healthcare industry
In the medical field, oxygen generators have become invaluable, particularly in home healthcare settings. Patients with chronic respiratory conditions, such as COPD or pulmonary fibrosis, often rely on supplemental oxygen for daily living. Portable oxygen generators provide a continuous supply, enhancing the patient’s quality of life and enabling greater mobility. Additionally, in hospitals, oxygen generators ensure a reliable and uninterrupted oxygen supply, crucial during surgeries or in intensive care units where patients may require high concentrations of oxygen.
Beyond healthcare, oxygen generators play a significant role in various industrial applications. In the field of aquaculture, for example, oxygen generation is essential for maintaining optimal conditions in fish farming. Adequate oxygen levels in water are critical for fish health and growth, and oxygen generators help ensure these levels are maintained. Similarly, in industries such as metal fabrication and chemical processing, pure oxygen is often required for efficient combustion processes, enhancing productivity and reducing emissions.
Environmental applications of oxygen generators are also emerging. In areas where natural oxygen levels are depleted, such as densely populated urban centers or regions impacted by pollution, these generators can help improve air quality. By increasing oxygen levels in these environments, they can potentially reduce health risks associated with low oxygen availability, promoting better overall well-being for residents. As technology advances, the integration of oxygen generators into various sectors is expected to expand, driving innovations that enhance efficiency, safety, and environmental sustainability.